Legacy Astronomical Images > Galactic Sources Series > Galactic Center Unit
Description
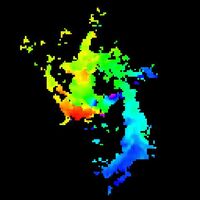
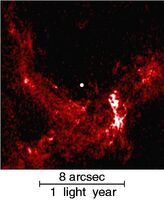
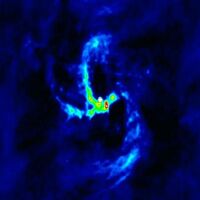
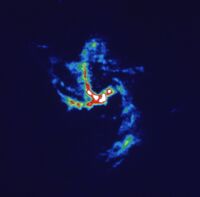
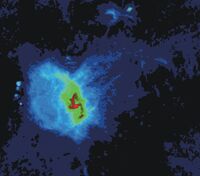
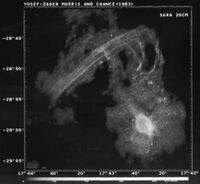
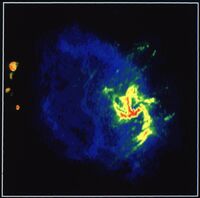
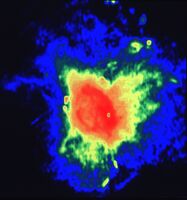
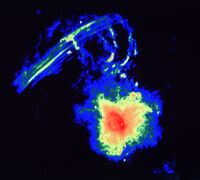
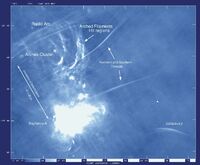
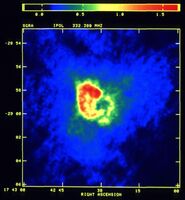
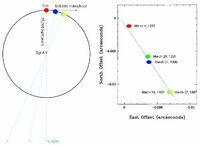
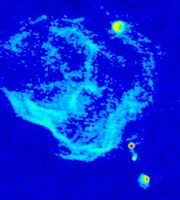
The center of our own Milky Way Galaxy is a whirlwind of activity. Stars at the Galactic center are born in clusters that are thousands of times more dense than what is typically seen in the disk of the Milky Way. Stars, along with molecular clouds and ionized gas, swirl around the very center of our Galaxy; around a black hole estimated to have the mass of a million suns.
Collection Items
Collection Tree
- Legacy Astronomical Images
- Legacy Astronomical Images > Galactic Sources Series
- Legacy Astronomical Images > Galactic Sources Series > Galactic Center Unit
- Legacy Astronomical Images > Galactic Sources Series