Atomic Gas in the 'Atoms for Peace' Galaxy
Description
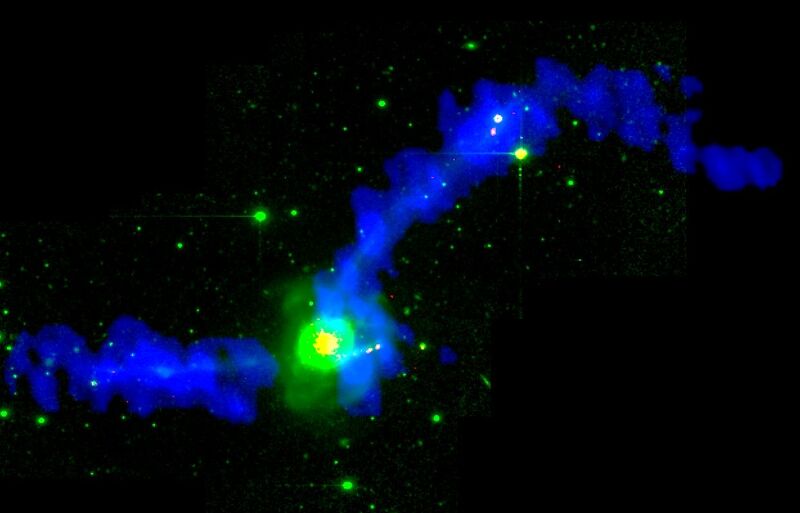
A composite image of the optical light (green), star forming regions (yellow and pink), and cold atomic hydrogen gas (blue) in the well known merger remnant NGC 7252, the "Atoms for Peace" galaxy. The nickname of this object derives from its optical appearance, specifically the pair of tidal tails (reminiscent of a peace sign) and the loops of material surrounding the optical body (reminiscent of early depictions of an atom). This system is the result of two spiral galaxies which collided and merged into a single object. The atomic hydrogen observations, taken with the VLA in its C- and D-array configurations, show the tidal tails to be rich in gas, confirming the gas-rich nature of the progenitor disks. They also show the inner regions to be relatively free of cold atomic gas. These observations support the idea that two gas-rich disk galaxies can merge together to form a circular gas-poor object similar to an early-type galaxy.
VLA C+D array observations with a resolution of 27"x16". Optical image is B-band image taken by P. Guhathakurta with the CTIO 4m telescope. The continuum subtracted Halpha image was taken using the KPNO 2.1m telescope.
Creator
Legacy Astronomical Images
Rights
NRAO/AUI/NSF does not hold full copyright for this image. Contact the archivist for details.
Type
Legacy Astronomical Image
Object Name
NGC7252
Photo Credit
J. Hibbard & J. van Gorkom
Investigators
J. Hibbard, J. van Gorkom
Telescope
Very Large Array (VLA)
Observation Date
1989-12-12
Type of Observation
spectral line
Wavelength
21 cm
Frequency
1420.4 MHz
Species
HI
Center of Image
RA 22:17:53.200, Dec: -24:54:26.000 (B1950)
Field of View
0.210000 x 0.125000 degrees
Link to journal article
Notes
Contact the archivist for a high resolution tif of this image.
Series
Galaxies Series
Unit
Peculiar Unit
Citation
Legacy Astronomical Images, “Atomic Gas in the 'Atoms for Peace' Galaxy,” NRAO/AUI Archives, accessed April 24, 2025, https://www.nrao.edu/archives/items/show/33558.