Cassiopeia A
Description
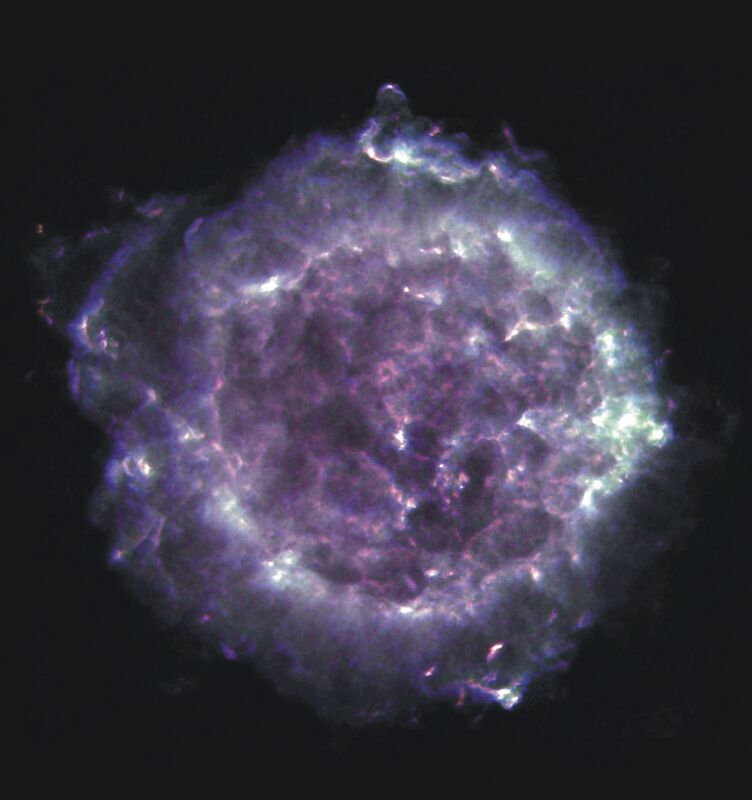
Cassiopeia A is the remnant of a supernova explosion that occured over 300 years ago in our Galaxy, at a distance of about 11,000 light years from us. Its name is derived from the constellation in which it is seen: Cassiopeia, the Queen. A supernova is the explosion that occurs at the end of a massive star's life; and Cassiopeia A is the expanding shell of material that remains from such an explosion. This radio image of Cassiopeia A was created with the National Science Foundation's Very Large Array telescope in New Mexico. This image was made at 3 different frequencies: 1.4 GHz (L band), 5.0 GHz (C band), and 8.4 GHz (X band). Cassiopeia A is one of the brightest radio sources in the sky, and has been a popular target of study for radio astronomers for decades. The material that was ejected from the supernova explosion can be seen in this image as bright filaments.
Creator
Legacy Astronomical Images
Rights
NRAO/AUI/NSF does not hold full copyright for this image. Contact the archivist for details.
Type
Legacy Astronomical Image
Object Name
Cassiopeia A
Photographer
Investigators
L. Rudnick, T. Delaney, J. Keohane & B. Koralesky
Telescope
Very Large Array (VLA)
Observation Date
1994-03-25
Type of Observation
continuum
Center of Image
RA 23:21:13.000, Dec: 58:32:35.000 (B1950)
Field of View
0.100000 x 0.100000 degrees
Notes
Contact the archivist for a high resolution tif of this image.
Series
Galactic Sources Series
Unit
Supernova Remnants Unit
Citation
Legacy Astronomical Images, “Cassiopeia A,” NRAO/AUI Archives, accessed April 1, 2025, https://www.nrao.edu/archives/items/show/33522.