SS 433 Radio / X-Ray Star
Description
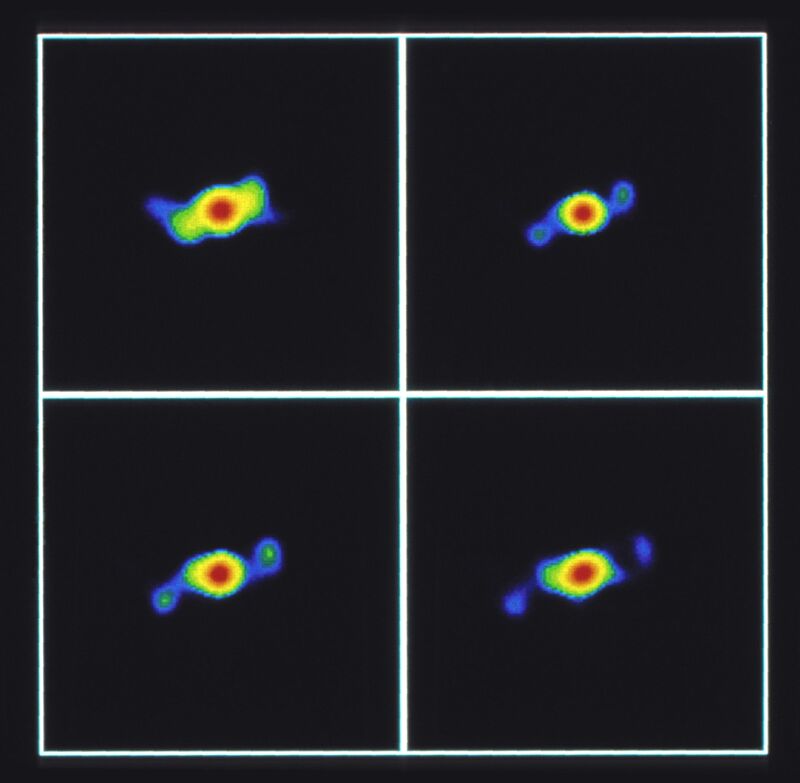
SS433 is an object known as an X-ray binary. X-ray binaries are systems of a "normal" star in orbit around a very dense massive compact object, a black hole or neutron star. In these systems there is frequently matter transfer from the normal star onto the compact object. This interaction of matter with the intense gravitational field of the black hole or neutron star causes the matter to heat up and produce X-rays, hence the name X-ray binary. SS433 is special because it is one of the few in this class to also exhibit jets of material ejected at speeds close to the speed of light on opposite sides of the system. This images shows four radio images of radio/x-ray star SS 433 made with the VLA in January, February, March, and April 1981. By examining differences in these images, astronomers infer that there are twin jets of material moving outwards from the central star system at speeds of 180 million mph, one fourth the speed of light.
The VLA was in the A-configuration using about 25 antennas.
Creator
Legacy Astronomical Images
Rights
NRAO/AUI/NSF does not hold full copyright for this image. Contact the archivist for details.
Type
Legacy Astronomical Image
Object Name
SS 433
Photo Credit
NRAO/AUI/NSF
Investigators
R.M. Hjellming, K.J. Johnston
Telescope
Very Large Array (VLA)
Observation Date
1981-02-18
Type of Observation
continuum
Center of Image
RA 19:11:50.000, Dec: 4:58:58.000 (J2000)
Field of View
0.003556 x 0.003556 degrees
Link to journal article
Notes
Contact the archivist for a high resolution tif of this image.
Series
Galactic Sources Series
Unit
Black Holes Unit
Citation
Legacy Astronomical Images, “SS 433 Radio / X-Ray Star,” NRAO/AUI Archives, accessed April 1, 2025, https://www.nrao.edu/archives/items/show/33426.