NGC 6764: A Radio Bubble Outflow
Description
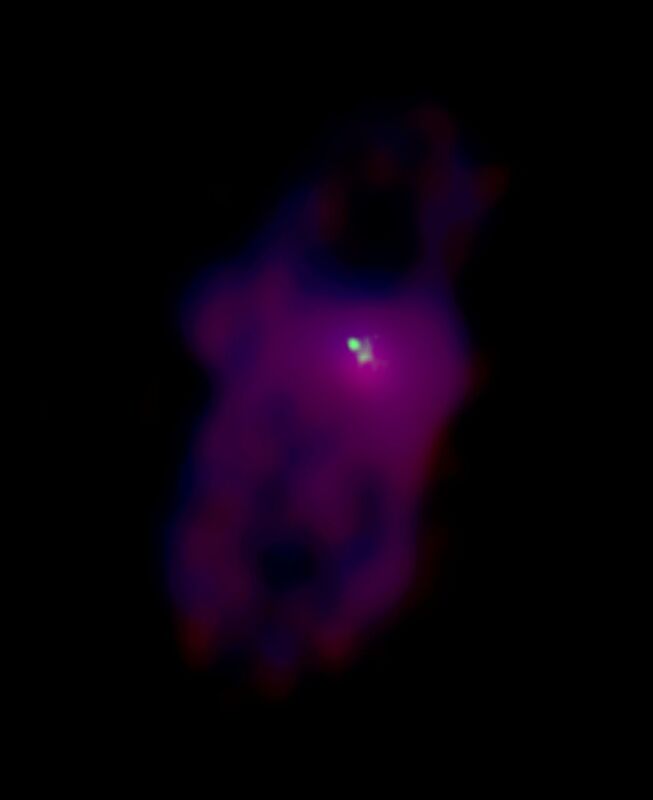
NGC6764 is a nearby Seyfert galaxy. The supermassive blackhole at the very centre of this AGN is producing relativistic radio plasma making this galaxy very bright in radio continuum. VLA image at 1.4GHz (in blue) as well as at 5GHz (in red) show a bright emission from the central region of the galaxy as well as bi-polar bubbles extending roughly in the north-south directions. Interestingly the position of the blackhole or the origin of its jet emission is seen as a bright point source in a high resolution image made with the VLA at 8GHz (in green). The plasma jet, probably directed in the east-west direction seems to have lost all its energy hitting the dense gas in the disk. Also there is an young starburst in the central region. Combined affect of the plasma from the jet and a possible young starburst driven Superwind is driving away a massive outflow of hot, warm, molecular and neutral atomic gas, and relativistic plasma perpendicular to the disk of the galaxy. Such outflows supply almost all metals to the inter-galactic medium.
Our own VLA A array observation at 1.4 GHz shown in blue our own VLA A array observation at 8 GHz shown in green Archival VLA B array observation at 5 GHz shown in red.
Creator
Legacy Astronomical Images
Rights
NRAO/AUI/NSF does not hold full copyright for this image. Contact the archivist for details.
Type
Legacy Astronomical Image
Object Name
NGC6764
Photo Credit
Ananda Hota, ASIAA, Taiwan and NRAO
Investigators
Ananda Hota, D. J. Saikia
Telescope
Very Large Array (VLA)
Observation Date
2003-08-12
Type of Observation
continuum
Center of Image
RA 19:8:16.400, Dec: 50:55:59.000 (J2000)
Field of View
0.010556 x 0.010556 degrees
Link to journal article
Notes
Contact the archivist for a high resolution tif of this image.
Series
Active Galactic Nuclei Series
Unit
Seyferts Unit
Citation
Legacy Astronomical Images, “NGC 6764: A Radio Bubble Outflow,” NRAO/AUI Archives, accessed April 20, 2025, https://www.nrao.edu/archives/items/show/33411.