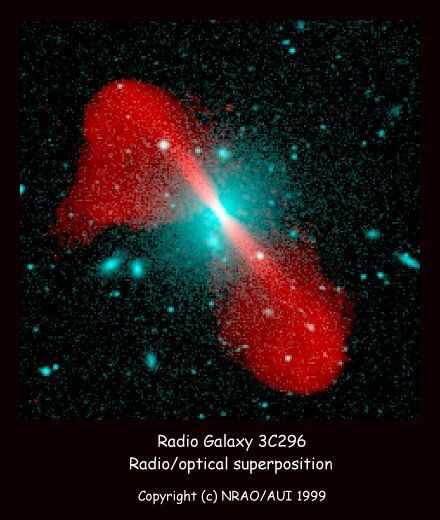
Radio Galaxy 3C296 Radio/Optical Superposition
Description
This is a false-color image of the radio galaxy 3C296, associated with the elliptical galaxy NGC5532. Blue colors show the distribution of stars, made from an image from the Digitized Second Palomar Sky Survey, and red colors show the radio radiation as imaged by the VLA, measured at a wavelength of 20cm. Several other galaxies are seen in this image, but are not directly related to the radio source. The radio emission is from relativistic streams of high energy particles generated by the radio source in the center of the radio galaxy. Astronomers believe that the jets are fueled by material accreting onto a super-massive black hole. The high energy particles are confined to remarkably well collimated jets, and are shot into extragalactic space at speeds approaching the speed of light, where they eventually balloon into massive radio lobes. The plumes in 3C296 measure 150 kpc or 480,000 light years edge-to-edge diameter (for a Hubble constant of 100 km/s/Mpc).
FR I (plumed) radio galaxy at z=0.0237. VLA 1.45 GHz image at 4.9 arcsec resolution.
Creator
Legacy Astronomical Images
Rights
NRAO/AUI/NSF does not hold full copyright for this image. Contact the archivist for details.
Type
Legacy Astronomical Image
Object Name
3C296
Photographer
Investigators
J.P. Leahy, R.A. Perley.
Telescope
Very Large Array (VLA)
Digitized Second Palomar Sky Survey
Observation Date
1987-12-02
Type of Observation
continuum
Band
L
Wavelength
20 cm
Frequency
1.4 GHz
Center of Image
RA 14:16:53.200, Dec: 10:48:11.000 (J2000)
Field of View
0.133300 x 0.133300 degrees
Link to journal article
Series
Active Galactic Nuclei Series
Unit
Radio Galaxies Unit
Citation
Legacy Astronomical Images, “Radio Galaxy 3C296 Radio/Optical Superposition,” NRAO/AUI Archives, accessed April 20, 2025, https://www.nrao.edu/archives/items/show/33368.