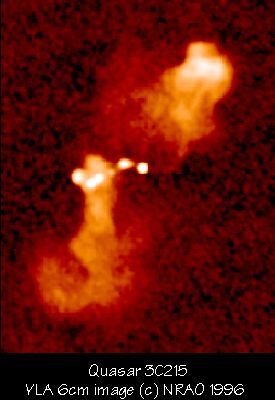
Radio Quasar 3C215
Description
This image shows the radio emission from relativistic streams of high energy particles generated by the quasar. Astronomers believe that the jets are fueled by material accreting onto a super-massive black hole at the center of the host galaxy (not shown in this image). The high energy particles are shot into extragalactic space at speeds approaching the speed of light, where they eventually balloon into massive radio lobes. The overall linear size of the radio structure is 196/h kpc (Hubble constant H = 100h km/s/Mpc). This quasar shows an unusual plume-like structure. The jet is extremely twisted and knotty, and there is a possible bent counterjet in the North lobe. The structure is unusually distorted on all scales.
This quasar is at a redshift z=0.411. VLA 4.9 GHz image at 0.9 arcsec resolution.
Creator
Legacy Astronomical Images
Rights
NRAO/AUI/NSF does not hold full copyright for this image. Contact the archivist for details.
Type
Legacy Astronomical Image
Object Name
3C215
Investigators
Alan H. Bridle, David H. Hough, Colin J. Lonsdale, Jack O. Burns, Robert A. Laing
Telescope
Very Large Array (VLA)
Observation Date
1987-07-11
Type of Observation
continuum
Band
C
Wavelength
6 cm
Frequency
5.0 GHz
Center of Image
RA 9:6:31.880, Dec: 16:46:11.700 (J2000)
Field of View
0.016700 x 0.016700 degrees
Link to journal article
Series
Active Galactic Nuclei Series
Unit
Quasars Unit
Citation
Legacy Astronomical Images, “Radio Quasar 3C215,” NRAO/AUI Archives, accessed April 1, 2025, https://www.nrao.edu/archives/items/show/33348.