Supernova of 386 AD
Description
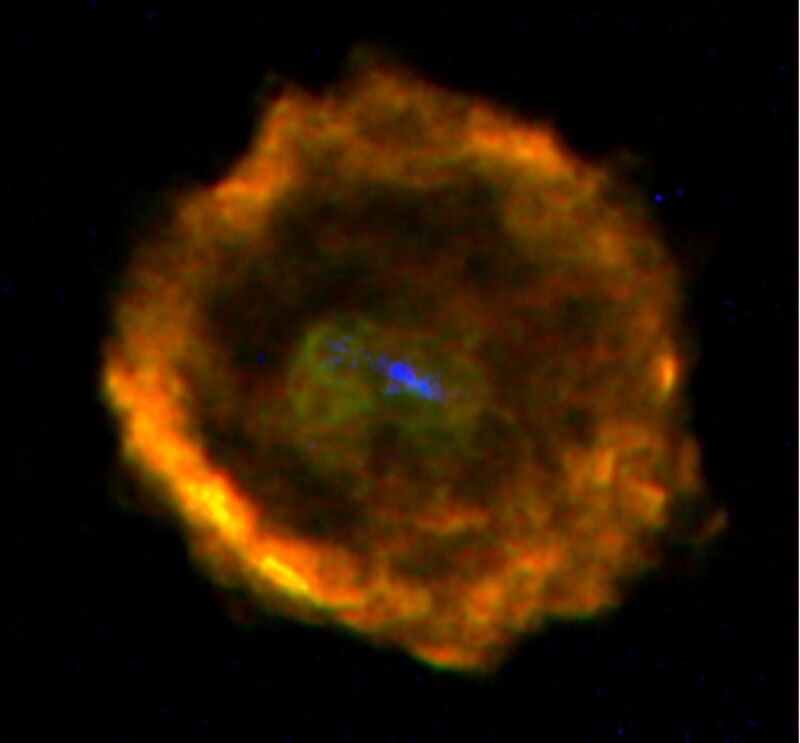
This composite radio and X-ray image shows G11.2-0.3, the remnant of a supernova observed by Chinese astrologers in 386 A.D. as a "guest star" in the Nan-tou Asterism. The radio data were obtained by scientists studying this supernova remnant with the NRAO Very Large Array at wavelengths of 20 cm (red) and 3.6 cm (green). The bubble in the remnant's center is greener than the outer shell because a central nebula is being created by a powerful wind coming off the pulsar at almost the precise center of the shell. This pulsar spins 15 times per second and the energetic electrons created by the wind can be seen in the Chandra X-ray Observatory image (blue). This astronomical object is a textbook example of a Type II supernova remnant created by the collapse of a massive star's core into a neutron star. G11.2-0.3 is sometimes called "The Turtle" because of its nearly perfect shell and because the pulsar is moving unusually slow.
Creator
Legacy Astronomical Images
Rights
NRAO/AUI/NSF does not hold full copyright for this image. Contact the archivist for details.
Type
Legacy Astronomical Image
Object Name
386AD
Investigators
Mallory Roberts (Eureka Scientific, Inc.), Cindy Tam (McGill University)
Telescope
Very Large Array (VLA)
Type of Observation
continuum
Band
X
Wavelength
3.6 cm
Frequency
8.4 GHz
Center of Image
RA 18:11:30.000, Dec: -19:25:30.000
Field of View
0.091667 x 0.091667 degrees
Notes
Contact the archivist for a high resolution tif of this image.
Series
Galactic Sources Series
Unit
Supernovae Unit
Citation
Legacy Astronomical Images, “Supernova of 386 AD,” NRAO/AUI Archives, accessed April 20, 2025, https://www.nrao.edu/archives/items/show/33530.